What Is the Common Cold and Why Does It Affect Some People More Than Others?
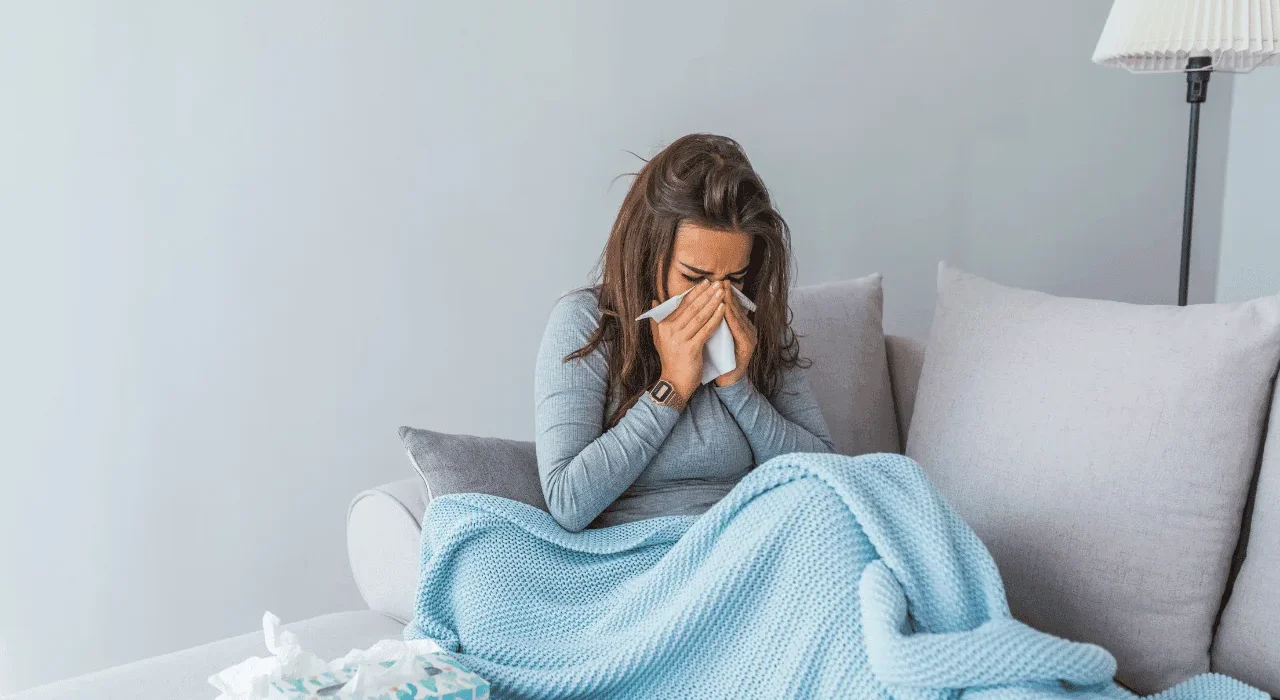
The common cold is one of the most widespread illnesses, affecting millions of people around the world each year. Although it is generally mild, it can still cause discomfort and disrupt daily life. Understanding what the common cold is and why some individuals are more prone to it can help in prevention and management.
What Is the Common Cold?
The common cold is a viral infection that affects the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, throat, and sinuses. It is caused by a variety of viruses, with the rhinovirus being the most common culprit.
Key Characteristics of the Common Cold:
- Typically lasts 7 to 10 days.
- Highly contagious, spreading through respiratory droplets, direct contact, or touching contaminated surfaces.
- Mild in most cases but can lead to complications like sinus infections or ear infections, especially in vulnerable individuals.
Also read:- What Is Asthma and Why Do Some People Develop It?
Symptoms of the Common Cold
The symptoms of a cold usually develop gradually and include:
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Sneezing
- Mild fever
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Mild body aches
Symptoms vary from person to person and can sometimes overlap with other illnesses, such as the flu or allergies.
Also read:- What Is Bronchitis and Why Do Some People Experience It More Often?
Why Do Some People Get Colds More Often?
Several factors contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to catching colds:
1. Immune System Strength
- A weakened immune system makes it harder to fight off cold viruses. This can be due to:
- Poor nutrition
- Lack of sleep
- Chronic stress
2. Age
- Young children are more likely to catch colds because their immune systems are still developing.
- Older adults may also be at higher risk due to age-related weakening of the immune system.
3. Exposure to Viruses
- People in crowded environments, such as schools, workplaces, or public transportation, are exposed to cold viruses more frequently.
- Those in close contact with sick individuals are at increased risk.
4. Seasonal Factors
- Colds are more common during the fall and winter months due to:
- Spending more time indoors in close proximity to others.
- Dry air, which can dry out nasal passages and make it easier for viruses to enter.
5. Lifestyle and Habits
- Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can irritate the respiratory tract, making it more susceptible to infection.
- Poor hygiene, such as not washing hands regularly, increases the risk of catching colds.
Also read:- 12 Questions to Ask Your Homeopath Before Starting Treatment
How to Prevent the Common Cold
While it’s impossible to avoid cold viruses entirely, certain steps can reduce your risk:
1. Practice Good Hygiene
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Use hand sanitizer when soap and water are unavailable.
2. Strengthen Your Immune System
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Get adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night for adults).
- Exercise regularly to boost overall health.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
3. Avoid Close Contact with Sick Individuals
- Maintain distance from people showing cold symptoms.
- Disinfect commonly touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, phones, and keyboards.
4. Stay Hydrated
- Drink plenty of water to keep mucous membranes moist and better equipped to trap viruses.
Managing Cold Symptoms
If you catch a cold, the following remedies can help alleviate symptoms and speed up recovery:
- Rest: Allow your body to recover by getting plenty of rest.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink water, herbal teas, and clear broths to soothe the throat and prevent dehydration.
- Use Over-the-Counter Medications: Decongestants, antihistamines, and pain relievers can provide temporary relief.
- Gargle Salt Water: This can ease a sore throat.
- Use a Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can relieve nasal congestion.
When to See a Doctor
Most colds resolve on their own, but you should seek medical attention if you experience:
- Symptoms lasting more than 10 days or worsening over time.
- High fever (above 102°F or 39°C).
- Severe sinus pain or swollen lymph nodes.
- Difficulty breathing or persistent chest pain.
These could be signs of complications like sinusitis, bronchitis, or pneumonia.
Conclusion
The common cold is a part of life for most people, but understanding its causes and risk factors can help reduce its impact. By practicing good hygiene, boosting your immune system, and managing symptoms effectively, you can minimize discomfort and recover faster. If cold symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Remember, staying proactive in prevention is the best way to keep the common cold at bay.