Understanding Tonsillitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Tonsillitis is a common condition that affects people of all ages, particularly children. It occurs when the tonsils, two oval-shaped pads of tissue located at the back of the throat, become inflamed. Tonsillitis can cause discomfort and disrupt daily life, but with the right treatment and care, most cases can be managed effectively. In this blog, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for tonsillitis, as well as tips for prevention.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Tonsillitis?
The tonsils are part of the immune system and play a role in protecting the body from infections. However, they can sometimes become overwhelmed by bacteria or viruses, leading to inflammation known as tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis can be:
Acute: Symptoms last for a few days to two weeks.
Chronic: Recurring episodes of tonsillitis over an extended period.
Recurrent: Multiple episodes within a year.
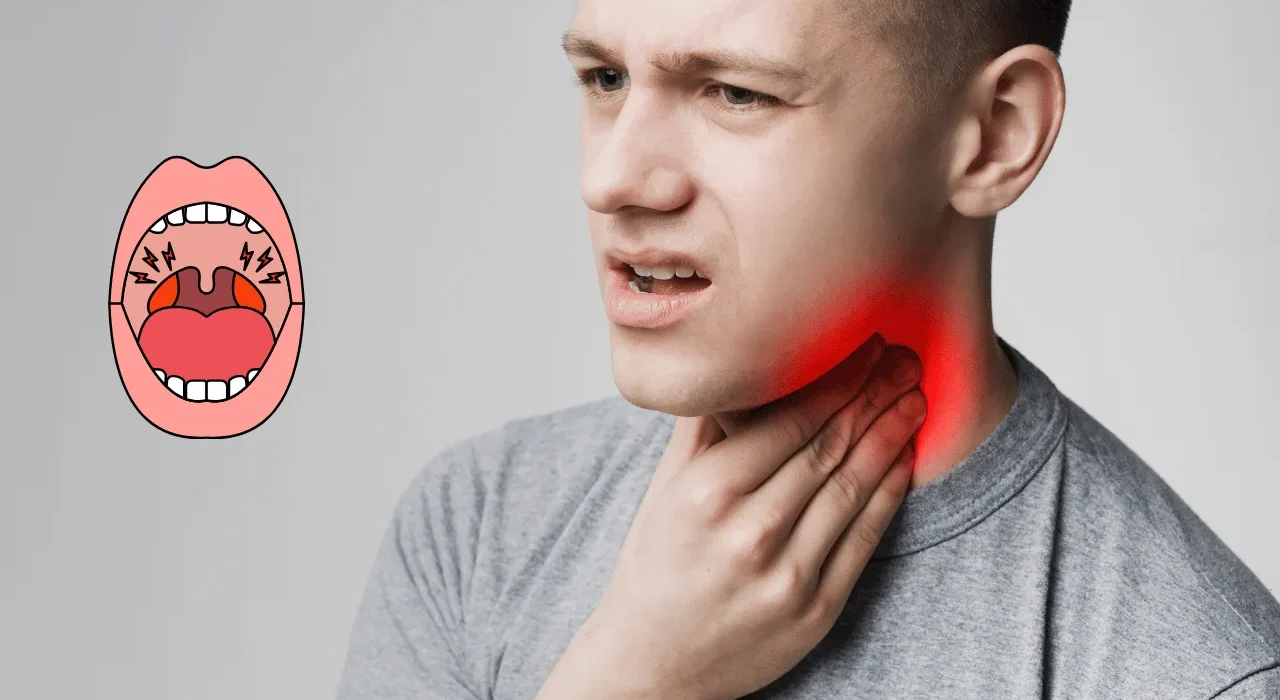
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
The symptoms of tonsillitis may vary depending on the severity of the condition, but common signs include:
Sore throat
Difficulty swallowing
Red, swollen tonsils
White or yellow patches on the tonsils
Fever and chills
Bad breath
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
Hoarseness or loss of voice
In children, additional symptoms like irritability, loss of appetite, and excessive drooling may occur
Causes of Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is usually caused by:
Viral Infections:
Common cold viruses
Influenza
Epstein-Barr virus (causes mononucleosis)
Bacterial Infections:
Group A Streptococcus (strep throat)
Tonsillitis caused by bacteria is less common than viral tonsillitis but may require antibiotic treatment.
Diagnosis of Tonsillitis
To diagnose tonsillitis, a healthcare provider may:
Conduct a Physical Examination:
Check for redness, swelling, or patches on the tonsils.
Perform a Throat Swab:
Collect a sample to test for bacterial infections like strep throat.
Blood Tests:
In cases of suspected mononucleosis or other viral infections.
Treatment for Tonsillitis
1. Home Remedies and Self-Care:
Rest and hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
Gargle with warm salt water: Helps soothe a sore throat.
Use throat lozenges: Provides temporary relief.
Over-the-counter pain relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and fever.
2. Medical Treatment:
Antibiotics: Prescribed if the tonsillitis is caused by a bacterial infection.
Surgery (Tonsillectomy): Recommended for recurrent or chronic tonsillitis, or when complications arise.
3. Supportive Therapies:
Use a humidifier to keep the air moist.
Avoid irritants like cigarette smoke or strong odors.
Complications of Untreated Tonsillitis
If left untreated, tonsillitis can lead to complications such as:
Peritonsillar abscess (a collection of pus near the tonsils)
Spread of infection to surrounding tissues
Difficulty breathing or swallowing
Rheumatic fever (in cases of untreated strep throat)
Preventing Tonsillitis
While not all cases of tonsillitis can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
Practicing good hygiene: Wash your hands frequently to prevent the spread of germs.
Avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
Keeping personal items like utensils and toothbrushes separate.
Strengthening your immune system with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Conclusion
Tonsillitis is a common condition that can cause significant discomfort, but it is typically manageable with the right approach. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and speed up recovery. If you or your child experience persistent symptoms of tonsillitis, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate care. Remember, maintaining good hygiene and a healthy lifestyle can go a long way in preventing infections like tonsillitis.