What Is Alopecia and Why Do Some People Experience Hair Loss?
Alopecia, a term used to describe hair loss, is a condition that affects millions of people globally. While it’s often associated with aging, alopecia can occur at any age and for various reasons. For some, it’s a temporary issue, while for others, it can lead to permanent hair loss. But what exactly is alopecia, and why are some individuals more susceptible to it than others? Let’s explore.
What Is Alopecia?
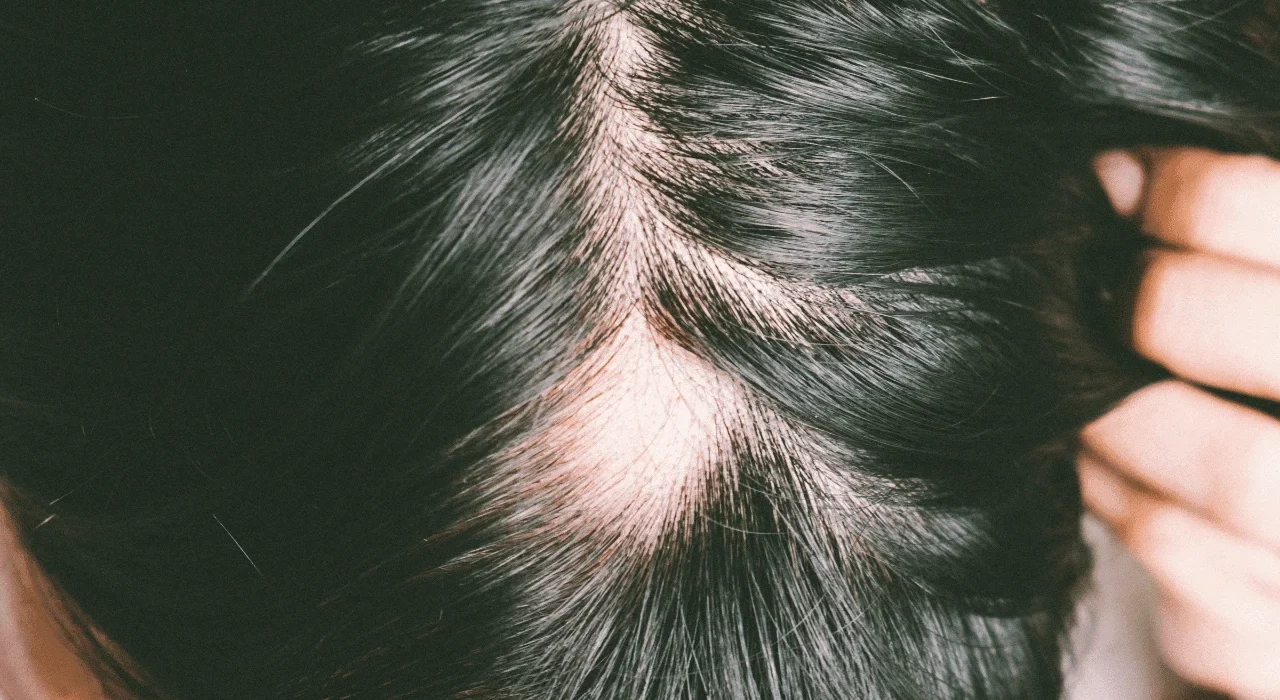
Alopecia refers to hair loss that can affect the scalp, face, or even the entire body. The condition occurs when the hair follicles, the structures in the skin that produce hair, are disrupted or damaged. This disruption may be caused by genetics, immune system activity, or external factors.
Also read:- Hair Fall Treatment in Abu Dhabi with Homeopathy
There are several types of alopecia, each with unique characteristics:
1. Androgenetic Alopecia
- Also known as male or female pattern baldness.
- The most common form of hair loss, caused by genetic and hormonal factors.
- Characterized by a receding hairline and thinning hair on the crown in men, and diffuse thinning in women.
2. Alopecia Areata
- An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles.
- Causes round, smooth patches of hair loss on the scalp, face, or body.
- In severe cases, it can progress to total hair loss on the scalp (alopecia totalis) or the entire body (alopecia universalis).
3. Telogen Effluvium
- A temporary form of hair loss caused by stress, illness, or hormonal changes.
- Leads to excessive shedding of hair during the telogen (resting) phase of the hair growth cycle.
4. Traction Alopecia
- Hair loss caused by prolonged tension on the hair due to tight hairstyles like braids, ponytails, or extensions.
- Can lead to permanent hair loss if not addressed early.
5. Cicatricial Alopecia
- A rare condition where inflammation damages hair follicles and replaces them with scar tissue, leading to permanent hair loss.
Also read:- Top 10 Health Conditions Treated by Homeopathy at Rise and Shine Clinic
Why Do Some People Experience Alopecia?
Alopecia doesn’t affect everyone equally, and its causes can vary widely. Here are the main factors:
1. Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in conditions like androgenetic alopecia. If hair loss runs in your family, you’re more likely to experience it.
2. Autoimmune Disorders
Conditions like alopecia areata occur when the immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles. Autoimmune disorders often have a genetic component but can also be triggered by stress or environmental factors.
3. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal imbalances, such as those experienced during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders, can lead to hair loss.
4. Stress and Trauma
Emotional or physical stress can push more hair follicles into the telogen phase, leading to noticeable shedding. Sudden weight loss, surgery, or illnesses can also trigger telogen effluvium.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients like iron, zinc, biotin, and protein can weaken hair and cause it to fall out.
6. Medical Treatments
Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and certain medications (like those for high blood pressure or depression) can disrupt hair growth and cause temporary or permanent hair loss.
7. Hairstyling Practices
Frequent use of tight hairstyles, harsh chemicals, or heat styling can damage hair follicles over time, resulting in traction alopecia.
How to Manage and Treat Alopecia
Although hair loss can be distressing, several management and treatment options are available:
1. Medications
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): A topical treatment that can slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
- Finasteride (Propecia): An oral medication for androgenetic alopecia in men.
- Corticosteroids: Used to reduce inflammation in autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata.
2. Lifestyle Changes
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support healthy hair growth.
- Reduce stress through activities like yoga, meditation, or regular exercise.
3. Hair Restoration Procedures
- Hair Transplants: Involves moving hair from one part of the scalp to another.
- Scalp Micropigmentation: A cosmetic procedure to create the appearance of hair.
4. Wigs and Hairpieces
For those with extensive hair loss, wigs and hairpieces offer a practical and stylish solution.
5. Support Groups and Counseling
Coping with hair loss can be emotionally challenging. Joining support groups or seeking therapy can help build resilience and confidence.
Conclusion
Alopecia is a complex condition influenced by genetics, health, lifestyle, and environmental factors. While it can be a source of distress, understanding the causes and exploring treatment options can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Remember, hair loss doesn’t define you, and solutions are available to help you feel your best.
If you’re experiencing hair loss, consult a dermatologist to determine the cause and create a tailored treatment plan. With the right approach, you can regain control and confidence.