Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
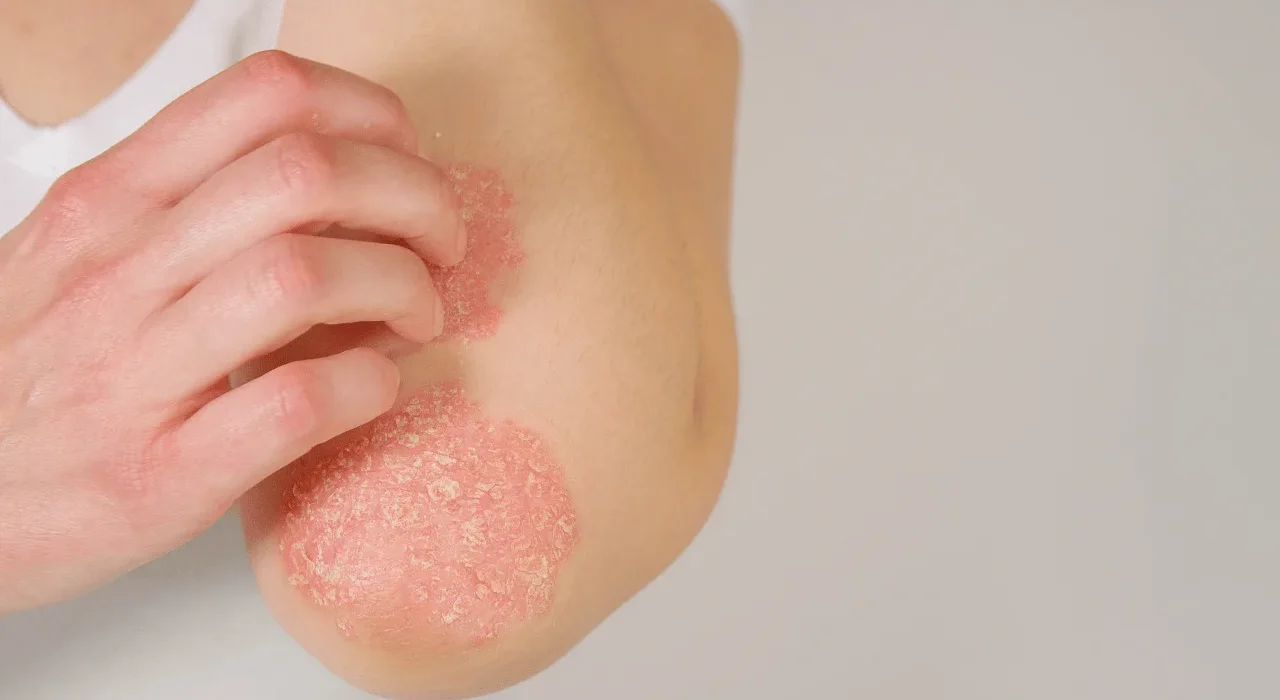
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, causing red, scaly patches that can be itchy, painful, and sometimes debilitating. Affecting millions of people worldwide, psoriasis can have both physical and emotional impacts. In this blog, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, types, and available treatments for psoriasis, as well as tips for managing the condition effectively.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis occurs when the immune system triggers an accelerated production of skin cells. Normally, skin cells regenerate over the course of a month, but in individuals with psoriasis, this process occurs in just a few days. This rapid turnover leads to a buildup of cells on the surface of the skin, forming the characteristic scaly patches.
While psoriasis is not contagious, it is a lifelong condition with periods of flare-ups and remission. It can affect people of any age but is most commonly diagnosed in adults.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis vary depending on its type, but common signs include:
Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
Itching, burning, or soreness in affected areas
Thickened or ridged nails
Pain or stiffness in joints (in cases of psoriatic arthritis)
Psoriasis commonly affects areas like the scalp, elbows, knees, lower back, and nails, but it can appear anywhere on the body.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each with distinct characteristics:
Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterized by raised, inflamed patches of skin with silvery-white scales.
Guttate Psoriasis: Appears as small, red spots, often triggered by infections like strep throat.
Inverse Psoriasis: Occurs in skin folds, such as under the breasts or around the groin, and is characterized by smooth, shiny lesions.
Pustular Psoriasis: Involves white pustules (blisters) surrounded by red skin.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare but severe form that causes widespread redness, scaling, and peeling of the skin.
Causes and Triggers
While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. Common triggers include:
Stress: Emotional stress can worsen symptoms.
Infections: Bacterial or viral infections may trigger flare-ups.
Medications: Certain drugs, such as beta-blockers or lithium, can aggravate psoriasis.
Injury to the Skin: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburn can lead to new patches (known as the Koebner phenomenon).
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, and obesity can exacerbate symptoms.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Although there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment options include:
1. Topical Treatments
Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
Vitamin D Analogues: Slow skin cell growth.
Coal Tar: Helps reduce scaling and inflammation.
Moisturizers: Keep the skin hydrated and minimize dryness.
2. Phototherapy
UVB Light Therapy: Uses ultraviolet light to slow skin cell growth.
PUVA Therapy: Combines a drug called psoralen with UVA light to improve symptoms.
3. Systemic Medications
For moderate to severe psoriasis, systemic treatments may be necessary:
Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
Methotrexate and Cyclosporine: Suppress the immune system to control symptoms.
Oral Retinoids: Help reduce the rapid growth of skin cells.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Psoriasis
In addition to medical treatments, adopting certain lifestyle changes can help manage psoriasis:
Healthy Diet: Focus on anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
Avoid Triggers: Identify and minimize exposure to known triggers.
Proper Skincare: Use gentle, fragrance-free products to prevent irritation.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help keep your skin healthy.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with psoriasis can be emotionally challenging. Support groups, counseling, and open communication with loved ones can help individuals cope with the mental health aspects of the condition. Sharing experiences and connecting with others who understand the challenges of psoriasis can provide valuable support.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to management. With proper treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support, individuals with psoriasis can lead fulfilling lives. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of psoriasis, consult a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in managing the condition effectively.